
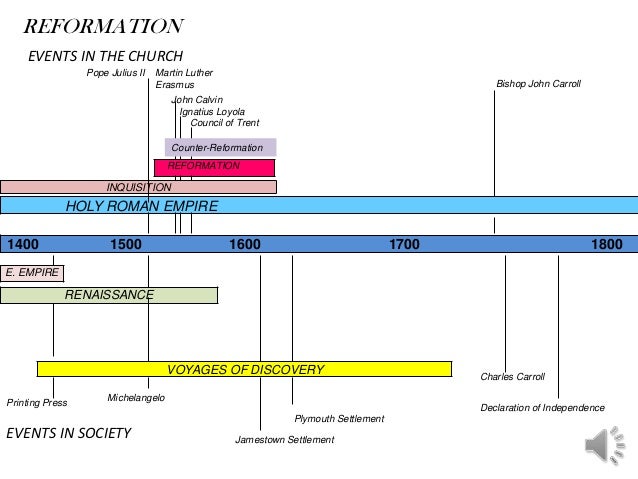
The church owned much land, held by monasteries, by church dignitaries, and by the churches themselves. The church also had great influence in shaping feudalism although the organization of the church was not feudal in character, its hierarchy somewhat paralleled the feudal hierarchy. By these processes feudalism became fixed in Frankish lands by the end of the 10th cent. Local royal officers and great landholders increased their power and forced the king to grant them rights of private justice and immunity from royal interference. More and more, this service-and-protection contract came to involve the granting of a beneficium, the use of land, which tended to become hereditary. The development of fiefs was also influenced by the Roman institution of patricinium and the German institution of mundium, by which the powerful surrounded themselves with men who rendered them service, especially military service, in exchange for protection. It was also possible for the manorial system to develop from the Germanic village, as in England. Increasingly, the poor landholder transferred his land to a protector and received it back as a precarium, thus giving rise to the manorial system. Important in an economic sense was the Roman villa, with the peculiar form of rental, the precarium, a temporary grant of land that the grantor could revoke at any time. The system used and altered institutions then in existence. Of course, the rise of feudalism in areas formerly dominated by Roman institutions meant the breakdown of central government but in regions untouched by Roman customs the feudal system was a further step toward organization and centralization. A long dispute between scholars as to whether its institutional basis was Roman or Germanic remains somewhat inconclusive it can safely be said that feudalism emerged from the condition of society arising from the disintegration of Roman institutions and the further disruption of Germanic inroads and settlements. It was the final 'nail in the coffin' of the Medieval Feudal System, feudalism, in England.Įach section of this Middle Ages website addresses all topics and provides interesting facts and information about these great people and events in bygone Medieval times including Decline of Feudalism.The feudal system first appears in definite form in the Frankish lands in the 9th and 10th cent. This led to the establishment of the Church of England and the Dissolution of the Monasteries.
At the end of the Middle Ages King Henry VIII clashed with the Pope and England subsequently broke with the Catholic church of Rome and the power of the Pope. Under feudalism the King was answerable to the Pope. The threat of the Mercenaries led on to the employment of professional, trained soldiers - the Standing Armies and ultimately the end of Middle Ages feudalism in England.ĭecline of Feudalism - the end of Feudalism in England The Mercenaries had few allegiances, except to money, and these paid fighting men were feared throughout Europe. Life changed and Mercenaries were hired from all over Europe. The decline of feudalism came when rich nobles were allowed to pay for soldiers rather than to fight themselves. The Decline of Feudalism - the Standing Armies A centralised government was established.Nobles became weaker - the Kings took back their lands and power.Armed men were paid a wage and Medieval warfare was financed by taxes and loans.The Feudal Levy was unpopular and as time went by Nobles preferred to pay the King rather than to fight and raise troops.Land was rented and the rights of lords over labour decreased.Peasants moved away from the country into towns they were eventually allowed to buy their freedom.More trade saw the growth of more towns.Charters were granted but ignored by nobles The Peasants Revolt - Peasants realised their worth and demanded changes.The Black Death - this reduced the population of England by one third.England started to move from land based economy to a money based economy.The Crusades and travel during the Middle Ages opened new trade options to England.The reasons for the decline of Feudalism during the Medieval period of the Middle Ages included:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
